to Vietnam
Vietnam is a diverse country whose bustling street life, flavourful cuisine, gorgeous landscapes and historical sites will move visitors in equal measure. The country stretches from rice terraces and limestone islands to untouched beaches and lush swampland, featuring buzzing cities and quaint towns along the way. Its culture has a similar variety, featuring prominent Chinese and French influences, that attracts travellers from all over the world.
Some inspiration for Vietnam...
Classic Vietnam
9 day / 8 night itinerary
Hanoi – Halong – Hoi An – Ho Chi Minh City
Cambodia & Vietnam
10 day / 9 night itinerary
A few of our favourite
experiences...
Hanoi Guided Morning Walk Tour
Hanoi
This classic Hanoi tour explores hidden gems and must-see attractions around Vietnam’s capital, including an ancient citadel, a church with French and Catholic architectural influences, an 11th–century Taoist temple, the serene surroundings around the West Lake and much more. For the more food-inclined, there is also a chance to try Pho Cuon, which tastes similar to fresh spring rolls and a delicious local lunch. This tour ends with a captivating ride on traditional bicycle rickshaws called cyclos, perfect for photos and slow-moving sightseeing.
Discova the difference
A perfect way to observe local life, this walking tour takes you away from typical tourist hotspots and unveils the real Hanoi with its hidden alleys, busy markets and historic monuments.
Hoi An Countryside Half-Day Biking Tour
Hoi An
Explore Hoi An’s meandering lanes on this morning bike tour while passing by key landmarks like the iconic Japanese bridge in the UNESCO World Heritage Town. This trip will give you a chance to interact with locals and visit one of Hoi An’s most exquisite villages, where your 90-year-old host will share his vivid recollections of the Vietnam War. Take a ferry ride back to town and end the journey with a spectacular view of Hoi An’s scenic waterfront.
Discova the difference
This is a unique opportunity to see the lush Vietnam countryside by cycling along rice fields and vegetable farms and catching a glimpse of peaceful village life.
Things to Know
Capital City: Hanoi
Population: 96 Million
Language: Vietnamese (minority languages include Tay, Muong, Cham, Khmer)
Currency: The Vietnamese dong (VND or ₫) is the country’s official currency. ATMs are found throughout the country, accepting most debit and credit cards. There are numerous places, including banks, gold shops and money exchange stalls, that exchange USD, whilst most other major foreign currencies such as EUR, UK GBP and AUS can be exchanged at banks.
Most foreign citizens need to obtain a tourist visa in advance when travelling to Vietnam, with the exception of citizens of countries that are unilaterally exempted from visas. As of 15 August, citizens from the UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, Russia, Belarus, Japan, and South Korea are granted temporary, visa-free residence for 45 days upon arrival (these citizens can be considered for visa issuance and temporary residence extension according to regulations). ASEAN citizens will remain eligible for the 30-day exempted visa (except for those from the Philippines (21 days), and Brunei & Myanmar (14 days)).
Currently, there are two ways of obtaining a visa. Travellers entering Vietnam by air can apply for a Visa on Arrival (VOA) through a travel agent. They will then receive an approval letter with which they can obtain the visa and entry stamp at the airport. This is the fastest and cheapest process, however, it’s only possible to get a VOA when arriving by plane through one of the six international airports. The other option is to apply for a visa through the Vietnamese embassy or consulate in advance, or to apply for an e-visa, which is valid for 90 days, single or multiple entry. The e-visa is available to citizens from all countries.
As travel policies change regularly, it’s best to check the official government website for the latest regulations before visiting: https://www.xuatnhapcanh.gov.vn/
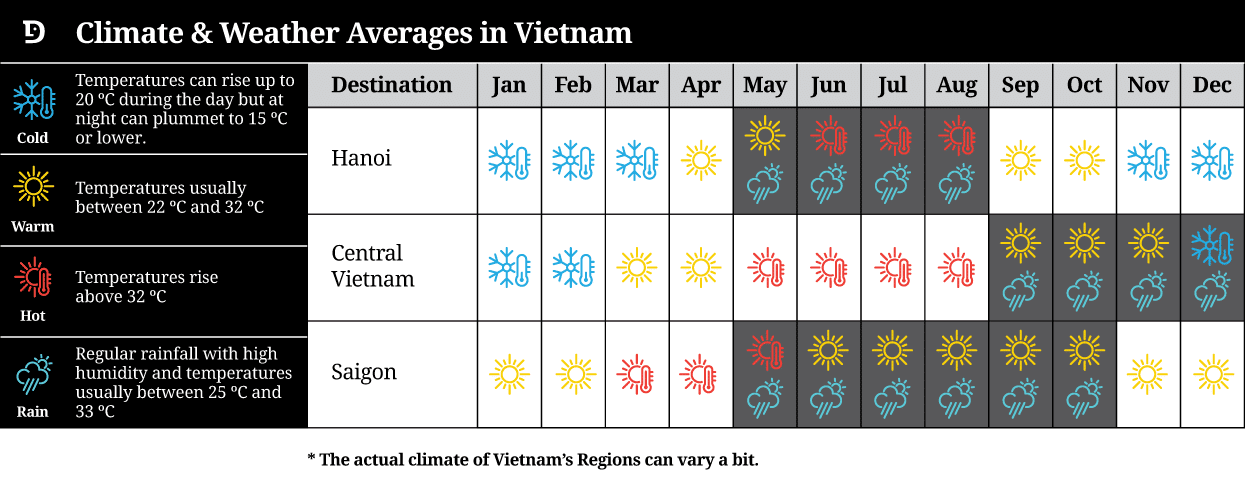
View or download our Vietnam Destination Guide
Want to know more?
If you’d like to find out more about Vietnam or get in touch with one of our agents, we’d love to hear from you!